

The DNA content of the precocious chromosomes in G1 is half the amount of the metaphase complement. Chromosomes condense during mitosis in most eukaryotes. The nuclear membrane is intact and nucleoli are present, to which some chromosomes are attached. This results in an expansion of the sperm into a. Answer to: When do chromosomes condense By signing up, you&039 ll get thousands of step-by-step solutions to your homework questions. Almost twice as many of these bands are produced as by trypsin treatment of metaphase chromosomes. First, condensed sperm chromatin is remodelled as sperm-specfic packaging proteins are evicted from DNA while core nucleosomes are assembled.
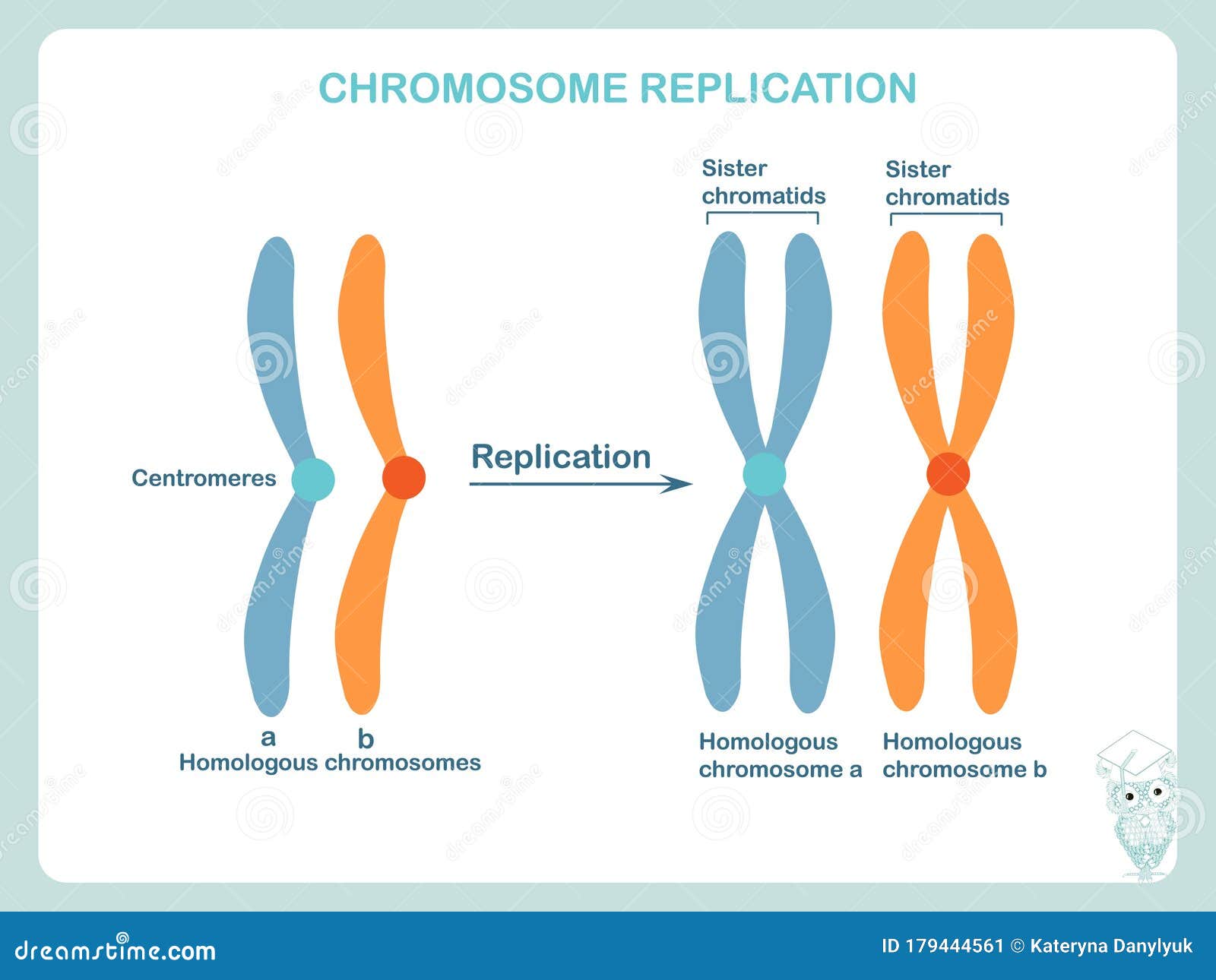
Some of the chromosomes are twice as long as the metaphase chromosomes and exhibit natural bands. Early chromatin condensation in interphase cells induced by mitotic cells only, consists of chromatids in the early or late G1 phase of the cell cycle that are not pulverized or fragmented at mitosis. The event, although similar in some ways to the phenomenon described as "premature chromosome condensation," "chromosome pulverization," and "prophasing," differs in that it does not require the presence of viruses and cell fusion before mitosis proceeds in the G1 cell. in which the chromosomes condense and subsequently separate into two. Early chromatin condensation in interphase cells (G1) of human peripheral blood lymphocytes has been induced without virus or cell fusion by exposure to allogeneic or xenogeneic mitotic cells. Anaphase Telophase Entry into Mitosis Chromosome Alignment Spindle PLK1 Aurora.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
